A Comprehensive Guide on Planting Sunflower Seeds Indoors
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on planting sunflower seeds indoors. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of growing sunflower seeds indoors, covering everything from choosing the right varieties to protecting your plants from frost. These flowers can brighten up any space, feed the birds, and make snacks for you with their seeds.

Sunflowers
Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus) are tall, annual plants native to North America, known for their large, bright yellow flower heads. These flowers consist of numerous smaller individual seeds arranged in a spiral pattern around a central disk. These Sunflowers are cultivated worldwide for their seeds, which are rich in oil and are commonly used for culinary purposes or as bird feed. Additionally, sunflowers are valued for their ornamental beauty and are often grown in gardens for their vibrant blooms, which attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
Starting sunflower seeds indoors
There are several different factors to consider before starting your sunflower seeds indoors. First, you will need to have the right equipment on hand and know the correct time to start the seeds indoors based on the time to transplant outside in your particular climate, or zone.
Some of the equipment needed to start seeds indoors are:
- Well-draining soil, potting mix, or seed-starting mix.
- A way to water.
- Indoor lights. There are a variety of ways to set up indoor lights.
- Pots, trays, or some kind of plant container of your choice. Some even save old yogurt containers and use them after thoroughly washing.
- The variety of seeds of your choosing.
Garden space of full sun
Your sunflowers will require full sun once transplanted outside. Their heads follow the movement of the sun throughout the day. They face east in the morning and by sunset, they are facing west. It is an amazing thing to witness over the growing season.
The best practice before sowing any seeds is to know where you plan to transplant them outside. If you have not already made a garden layout, I highly recommend you do so to give you the best chance of success for your sunflowers and anything else you plan to grow in and around that space.
Well-Drained Soil
Begin by selecting well-drained soil enriched with organic matter, creating an ideal environment for your sunflowers to develop robust root systems.
The foundation of any successful garden lies in its soil, and sunflowers are no exception. When embarking on your sunflower-growing journey, one of the first steps is to ensure you have well-drained soil in which to plant your seeds. Well-drained soil is essential for several reasons, chief among them being the promotion of healthy root development.
Why Well-Drained Soil Matters
Root Health
Sunflowers, like most plants, rely on a healthy root system to anchor themselves in the ground and absorb essential nutrients and water. Well-drained soil allows excess water to drain away efficiently, preventing the roots from becoming waterlogged and susceptible to rot. This encourages the development of robust, healthy root systems that can support the vigorous growth and blooming of your sunflowers.
Preventing Waterlogging
Waterlogged soil can spell disaster for sunflowers, causing root suffocation, fungal diseases, and stunted growth. By selecting well-drained soil, you mitigate the risk of waterlogging, ensuring that excess moisture is swiftly removed from the root zone and allowing air to circulate freely around the roots.
Nutrient Availability
In addition to water drainage, well-drained soil also plays a crucial role in nutrient availability. Organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, enriches the soil, providing essential nutrients that sunflowers need to thrive. However, if the soil is waterlogged, these nutrients may become inaccessible to the roots, hampering growth and flowering.
Creating an Ideal Environment
To create an ideal environment for your sunflowers, begin by selecting a planting site with well-drained soil. Avoid areas prone to waterlogging, such as low-lying or compacted soils. If your garden soil is heavy or poorly drained, consider amending it with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to improve drainage and fertility.
Tips for Ensuring Good Drainage:
– Incorporate organic matter: Mix in compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil structure and drainage.
– Avoid compacting the soil: Minimize foot traffic in the planting area to prevent soil compaction, which can impede drainage.
– Consider raised beds: If drainage issues persist, consider planting sunflowers in raised beds filled with well-draining soil mixtures.
– Mulch: Apply a layer of mulch around sunflower plants to help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature while still allowing excess water to drain away.
Selecting well-drained soil enriched with organic matter sets the stage for successful sunflower cultivation, providing optimal conditions for robust root development, efficient water drainage, and nutrient uptake. By prioritizing soil health, you’ll lay the groundwork for a thriving garden filled with vibrant, sun-kissed blooms.

Different varieties of sunflowers
Explore a variety of sunflowers, from dwarf varieties suitable for small spaces to mammoth sunflowers that reach impressive heights taller than some men. Consider tall varieties for a striking garden backdrop and a point of discussion for your friends and family who visit your garden.
The type of sunflower variety will be listed on your seed packet. You can buy these at any local garden nursery or online at places like MIGardener or Baker Creek.
Dwarf Varieties
These compact sunflowers are perfect for small spaces, making them ideal for container gardening or adorning tight corners of your garden. Despite their diminutive stature, dwarf sunflowers boast equally stunning blooms, offering a burst of color and cheerfulness wherever they’re planted. Their manageable size also makes them excellent choices for creating vibrant floral arrangements or adding a touch of sunshine to indoor spaces.
Tall Varieties
On the other end of the spectrum, tall sunflower varieties stand as towering sentinels in the garden landscape, commanding attention with their majestic presence. These giants can reach impressive heights, creating a dramatic backdrop against fences, and walls, or as focal points in larger garden beds. With their towering stalks and oversized blooms, tall sunflowers add a sense of grandeur and majesty to any outdoor setting, attracting admiration from both humans and pollinators alike.
Mammoth Sunflowers
If you’re seeking to make a bold statement with your garden, look no further than mammoth sunflowers. As their name suggests, these giant sunflowers boast enormous blooms and towering heights, making them the epitome of sunflower grandeur. Whether planted as standalone specimens or in a row to create a striking sunflower wall, mammoth sunflowers never fail to captivate onlookers with their sheer size and splendor. Additionally, their ample seed heads provide a bountiful harvest of nutritious seeds, perfect for snacking or feeding local wildlife.

Here are some popular sunflower varieties:
Mammoth’ Sunflower: Known for its massive size, with flower heads reaching up to 12 inches in diameter on stalks that can grow over 10 feet tall.
Russian Giant Sunflower: Similar to ‘Mammoth,’ this variety produces large flower heads and tall stalks, often reaching heights of 8 to 12 feet.
Autumn Beauty Sunflower: A multi-branched variety that produces an array of colorful blooms in shades of yellow, orange, and red, adding vibrant hues to the garden.
Lemon Queen’ Sunflower: This variety features soft yellow petals surrounding a dark center, creating a striking contrast. It typically grows to a height of 5 to 6 feet.
Teddy Bear Sunflower: A dwarf variety with fluffy, double blooms that resemble pom-poms. ‘Teddy Bear’ sunflowers are perfect for smaller gardens or containers.
Evening Sun’ Sunflower: Known for its unique coloration, with deep red petals that fade to golden yellow at the tips, creating a stunning sunset-like effect.
Ring of Fire Sunflower: This variety features fiery red and orange petals with dark centers, resembling a blazing ring of flames.
Velvet Queen’ Sunflower: With rich, burgundy-red petals and dark centers, ‘Velvet Queen sunflowers add a dramatic touch to garden borders and flower arrangements.
Sunforest Mix’ Sunflower: A blend of different sunflower varieties, including various colors, sizes, and petal shapes, creating a diverse and eye-catching display in the garden.
Dwarf Sungold’ Sunflower: A compact variety with golden-yellow flowers and dark centers, ideal for small spaces or as border plants in flower beds.
These are just a few examples of the many sunflower varieties available, each offering unique characteristics and beauty to enhance your garden landscape.
Soil Temperature and Risk of Frost
Monitor soil temperature, ensuring it aligns with the preferences of sunflowers (Helianthus annuus). Start planting at the best time, minimizing the risk of frost damage, especially in cooler climates. This will depend upon your specific zone. To find out what zone you’re in, you can Google “find my garden zone” and many different places will pop up asking for your zip code. I tend to use Almanac. I would also suggest you join local gardening groups which will have a better insight on when to plant your seedlings outside.
Importance of Soil Temperature
Soil temperature plays a crucial role in the successful germination and growth of sunflowers (Helianthus annuus). These warm-season plants have specific temperature preferences for optimal seed germination and root development. Monitoring soil temperature ensures that you provide the ideal conditions for your sunflower seeds to sprout and thrive.
Determining Soil Temperature:
There are several methods for measuring soil temperature:
Soil Thermometer
A soil thermometer is a useful tool designed for measuring soil temperature at various depths. Insert the thermometer into the soil at the desired depth and wait for a few minutes to obtain an accurate reading.
Digital Thermometer
Alternatively, you can use a digital thermometer with a soil probe attachment to measure soil temperature quickly and accurately.
Online Resources
Many gardening websites and apps offer soil temperature data for specific locations, allowing you to access real-time information and historical averages for your area.
Early Planting and Danger of Frost
Plant your sunflower seeds early, but be wary of the danger of frost. Provide sheltered spots or use plastic bottles with the bottoms removed as protective covers for young plants during colder nights.
Last Frost Date and Its Importance
Definition of a Last Frost Date
The last frost date, also known as the average final frost date or frost-free date, refers to the approximate date in spring when the risk of frost occurrence is considered to be minimal in a specific geographic area. It marks the end of the frosty period and signifies the transition to warmer temperatures conducive to plant growth.
Determining the Last Frost Date
The last frost date varies from region to region and depends on factors such as climate, elevation, and local weather patterns. Gardeners often rely on historical climate data, local agricultural extension services, or online resources to estimate the average last frost date for their area.
Significance for Gardeners
Understanding the last frost date is crucial for gardeners, as it informs planting schedules and helps mitigate the risk of frost damage to tender plants. Here’s why it’s important:
Planting Timing
The last frost date serves as a guideline for determining when it’s safe to plant frost-sensitive crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, and annual flowers, outdoors. Planting too early, before the last frost date, can expose young seedlings to freezing temperatures, leading to stunted growth, leaf damage, or plant death.
Protection Planning
By knowing the last frost date, gardeners can plan and take appropriate measures to protect tender plants from late spring frosts. This may involve covering plants with frost blankets, cloches, or row covers overnight to shield them from cold temperatures and prevent frost damage.
Optimizing Growing Season
Planting crops and flowers after the last frost date allows them to benefit from warmer temperatures and longer daylight hours, optimizing the growing season and promoting healthy growth and development. This timing maximizes the potential for abundant harvests and colorful blooms throughout the growing season.
Local Variations and Microclimates
While the last frost date provides a general guideline for garden planning, it’s essential to consider local variations and microclimates that may influence frost occurrence. Factors such as proximity to bodies of water, elevation changes, and urban heat islands can affect local climate conditions and alter frost risk patterns.
Minimizing the Risk of Frost Damage
In cooler climates, the risk of frost can pose a threat to young sunflower plants. To minimize the risk of frost damage:
Plant at the Right Time
Wait until soil temperatures consistently align with the preferences of sunflowers before planting seeds outdoors. Starting seeds too early can expose them to potential frost damage.
Protect Seedlings if Frost is Forecasted
If a late spring frost is forecasted after planting, take precautions to protect young seedlings. Cover them with cloches, row covers, or blankets overnight to insulate them from the cold and prevent frost damage.
The last frost date marks the end of the frosty period in spring and signals the onset of warmer growing conditions for gardeners. By knowing the last frost date for their area and understanding its significance, gardeners can make informed decisions about planting timing, protect tender plants from frost damage, and optimize the growing season for a successful and bountiful garden harvest.
Grow Lights and Their Role in Indoor Gardening
There are many different indoor grow light systems and endless possibilities to make your own setup. If you need help deciding what to buy or how to set up a grow light system, check out my post on starting seeds indoors for more information.
Supplementing Sunlight with Grow Lights
In indoor gardening, especially when sunlight is limited or inconsistent, grow lights play a vital role in providing the necessary light spectrum for plant growth. Sunflower seedlings, like many other plants, require ample light to develop strong stems and vibrant foliage. Supplementing natural sunlight with grow lights ensures that sunflower seedlings receive adequate light intensity and duration for healthy growth, even in indoor environments with limited access to sunlight.
Benefits of Using Grow Lights
Consistent Light Source
Grow lights offer a consistent light source that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of sunflower seedlings throughout their growth stages. Unlike natural sunlight, which may vary in intensity and duration depending on factors like weather and time of year, grow lights provide a reliable light source year-round, ensuring consistent growth and development.
Extended Growing Season
By using grow lights, indoor gardeners can extend the growing season for sunflowers and other plants beyond the limitations imposed by outdoor conditions. This allows for year-round gardening and the opportunity to cultivate sunflower varieties that may not thrive in your local climate or during certain times of the year.
Optimized Light Spectrum
Grow lights are designed to emit light across the entire spectrum needed for plant growth, including red, blue, and white wavelengths. This ensures that sunflower seedlings receive the optimal light spectrum required for photosynthesis, chlorophyll production, and overall plant health.
Controlled Environment
Indoor gardening with grow lights provides a controlled environment where factors such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity can be precisely regulated to create optimal growing conditions for sunflower seedlings. This level of control allows for experimentation with different growing techniques and plant varieties to maximize success.
Step-by-step instructions to start your sunflower seeds indoors:
1. Select Sunflower Varieties:
- Choose a variety of sunflower seeds suited to your indoor growing conditions and outdoor planting area. Consider factors such as available space, sunlight exposure, and desired height and flower color.

2. Prepare Planting Containers:
- Select suitable planting containers with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Use biodegradable pots, seed trays, or individual pots filled with well-draining potting mix.
3. Prepare Potting Mix:
- Use a high-quality potting mix or seed-starting mix that provides good aeration and drainage. Avoid heavy garden soil, as it may compact and hinder seedling growth.
- Moisten the soil in a bucket or large tote to a brownie-mix consistency.
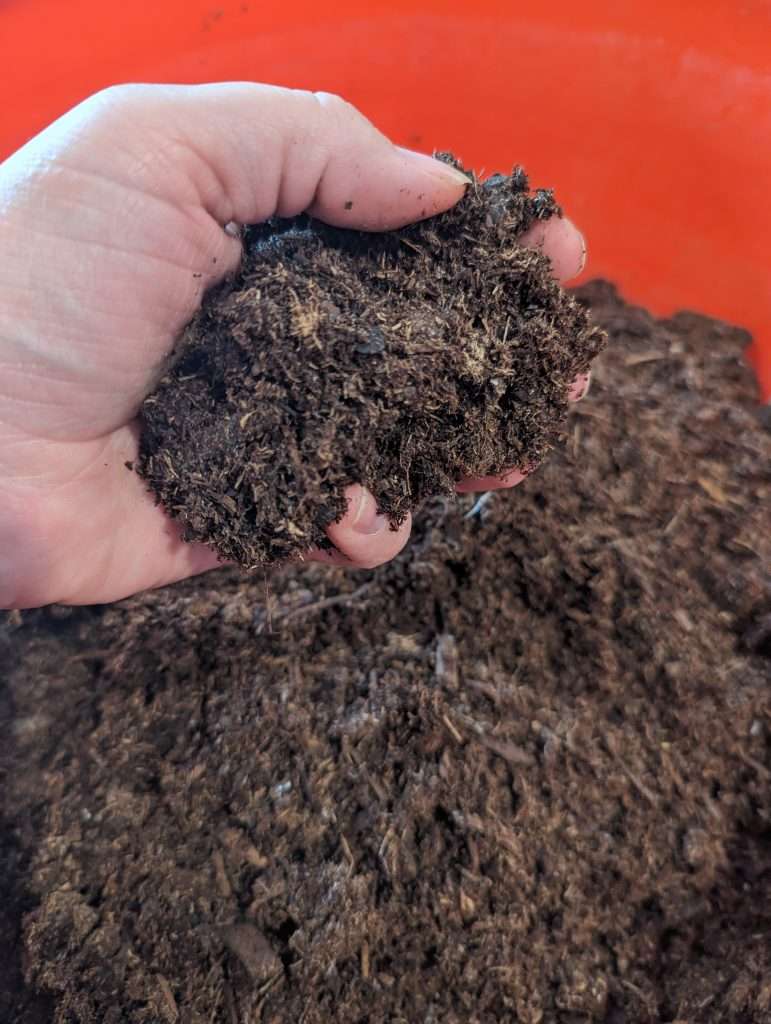

4. Create Small Holes:
- With your finger or a small tool, create small holes in the soil surface of each planting container. Space the holes according to the recommended planting distance for the chosen sunflower variety.
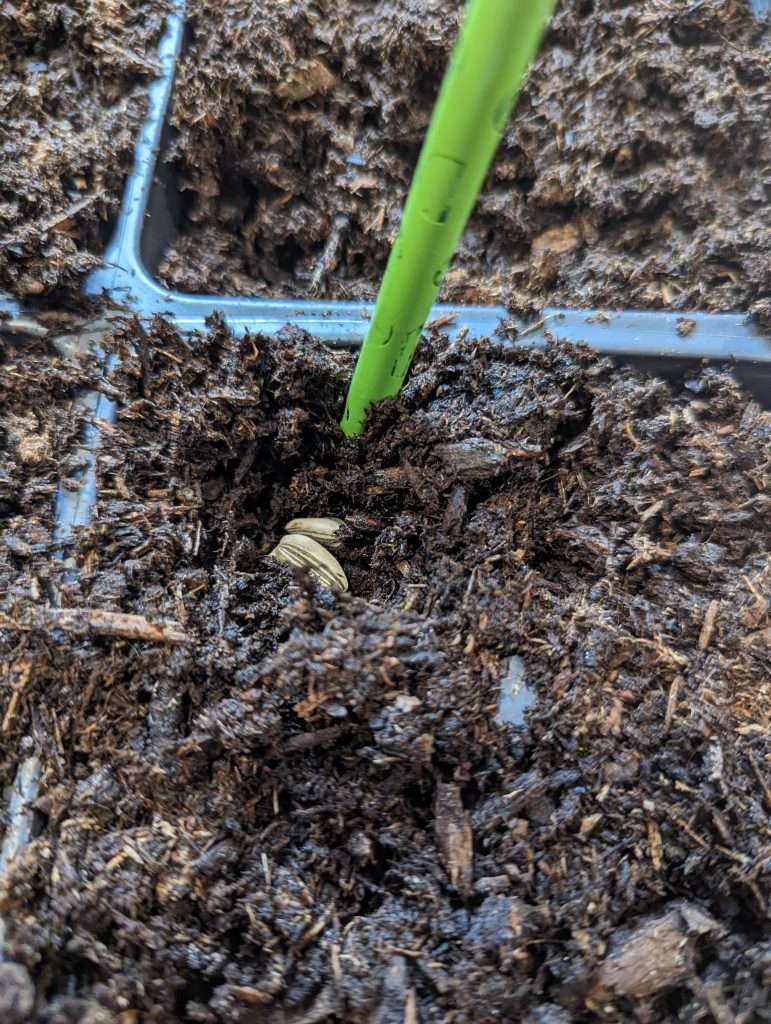

5. Sow Seeds at the Right Depth:
- Place one or two sunflower seeds into each hole, ensuring they are spaced evenly and not overcrowded. The depth at which you sow the seeds depends on the size of the seeds. As a general rule, sow seeds at a depth of about twice their diameter.
- Gently cover the seeds with soil, lightly pressing down to ensure good seed-to-soil contact.
6. Provide Adequate Light and Warmth:
- Place the planting containers in a warm, bright location with indirect sunlight or under grow lights. Sunflower seeds germinate best in temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C to 29°C). Maintain consistent moisture levels in the soil, but avoid overwatering.
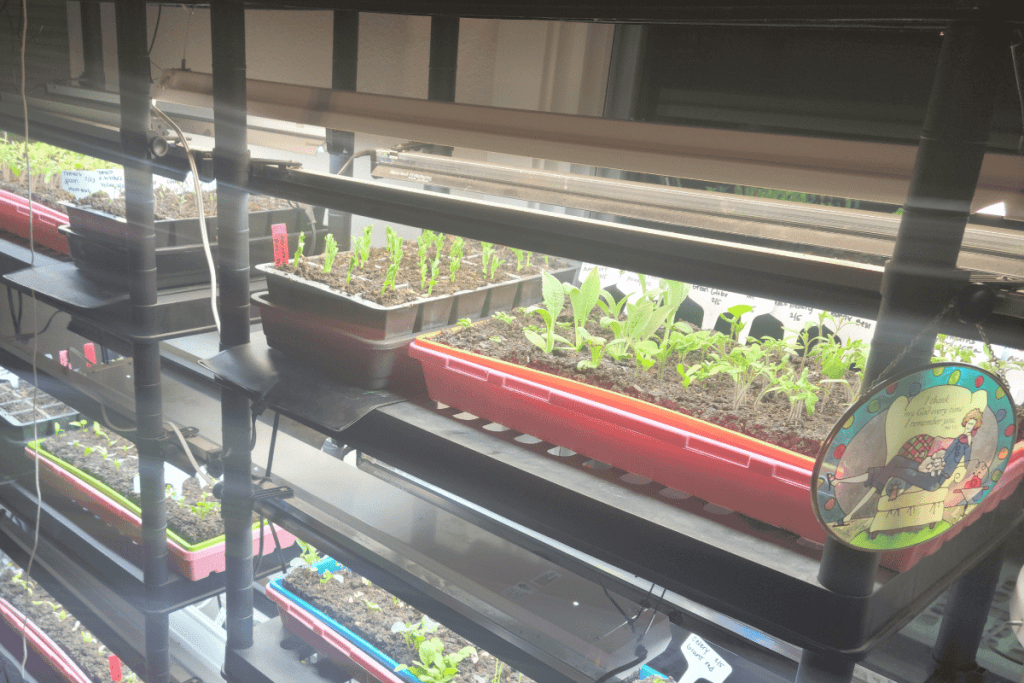

7. Monitor Germination and Growth:
- Keep a close eye on the planting containers for signs of germination, which typically occurs within 7 to 10 days, depending on the variety and environmental conditions. Once seedlings emerge, provide adequate light, warmth, and moisture to support healthy growth.
8. Harden Off Seedlings:
- As the sunflower seedlings grow and develop true leaves, gradually acclimate them to outdoor conditions through a process known as hardening off. Start by exposing the seedlings to outdoor conditions for short periods each day, gradually increasing the exposure throughout one to two weeks.
9. Transplant Outdoors:
- Once the risk of frost has passed and the sunflower seedlings have been hardened off, it’s time to transplant them into the garden. Choose a sunny location with well-drained soil and ample space for the mature size of the selected sunflower varieties.
- Dig holes in the planting area that are slightly larger than the root balls of the seedlings. Gently remove the seedlings from their containers and place them into the prepared holes, ensuring they are planted at the same depth as they were in the containers.
- Backfill the holes with soil and water the newly transplanted seedlings thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots.

By following these step-by-step instructions, you can successfully sow sunflower seeds indoors and transplant the seedlings outdoors, taking into account the specific planting area requirements of different sunflower varieties and your particular zone and climate. With proper care and attention, you’ll soon be enjoying the cheerful blooms of your sunflowers in your outdoor garden.
Other Things to Consider
Below are some other things to consider in more depth. These items will depend on your budget and the space you’re growing indoors in.
Container Selection and Size
When choosing containers for starting sunflower seeds indoors, consider factors such as drainage, size, and material. Opt for pots or trays with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging, and select sizes appropriate for the number of seeds being planted and the eventual size of the sunflower plants. Larger containers allow for more root growth and may reduce the need for transplanting until the seedlings are ready to be moved outdoors.
Seed-Starting Techniques
Explore various seed-starting techniques to improve germination rates and seedling vigor. Pre-soaking sunflower seeds in water for a few hours or overnight can soften the seed coat and encourage faster germination. For larger seeds, consider scarifying them by gently nicking or scratching the seed coat to promote better water absorption. When sowing seeds indoors, ensure proper spacing to prevent overcrowding and competition among seedlings.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels is crucial for successful seed germination and seedling growth indoors. Use heat mats or maintain ambient room temperature within the optimal range for sunflower seeds, typically between 70°F and 85°F (21°C to 29°C). Monitor humidity levels to prevent drying out or overly moist conditions, which can lead to damping off or fungal issues.
Watering Practices
Develop a watering routine that keeps the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Use a watering can with a fine spray or a misting bottle to water gently, avoiding disturbing the soil or seedlings. Check the moisture level regularly and adjust the watering frequency as needed based on environmental conditions and plant growth stage. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can stunt growth and lead to wilting.
Fertilization and Nutrient Needs
Provide sunflower seedlings with adequate nutrients to support healthy growth and development. Consider using a balanced fertilizer solution diluted to half strength or incorporating organic amendments such as compost or worm castings into the potting mix. Monitor plant growth and adjust fertilization practices accordingly, avoiding overfeeding, which can cause nutrient imbalances or fertilizer burn.
Pest and Disease Management
Be vigilant for common pests and diseases that may affect indoor sunflower seedlings, such as aphids, whiteflies, or fungal pathogens. Implement preventive measures such as inspecting plants regularly, maintaining cleanliness, and providing adequate airflow to reduce humidity and prevent fungal issues. Consider using natural remedies or organic pesticides to control pest infestations while minimizing harm to beneficial insects and the environment.
Support and Staking
For taller sunflower varieties, provide support or staking for indoor seedlings to prevent them from becoming top-heavy or lean as they grow. Install stakes or trellises in the containers and secure seedlings with soft ties or twine to prevent damage to stems or roots. Regularly check and adjust supports as needed to ensure proper alignment and stability as the seedlings mature.
Pruning and Thinning
Promote stronger growth and larger flower heads by pruning and thinning indoor sunflower seedlings as needed. Remove any damaged, diseased, or overcrowded seedlings to allow more space and resources for the remaining plants. Prune excessive foliage or stems to encourage airflow and reduce the risk of fungal diseases. Thin out seedlings to maintain proper spacing and prevent overcrowding, which can lead to competition for light, water, and nutrients.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Starting sunflower seeds indoors offers a rewarding opportunity to nurture healthy plants right from the comfort of your home and get an early start on your garden. By following this comprehensive guide outlined above, you can start a successful indoor gardening journey and experience the joy of watching sunflower seedlings thrive under your care.
From selecting the right containers and soil mixtures to providing optimal lighting, temperature, and humidity conditions, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of your indoor sunflower cultivation efforts. By paying attention to details such as watering practices, fertilization, and pest management, you can create an environment conducive to robust growth and vibrant blooms.
Remember to monitor the progress of your sunflower seedlings closely, adjusting care routines as needed to address any challenges that may arise along the way. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a novice enthusiast, starting sunflower seeds indoors offers a fulfilling experience that allows you to connect with nature and enjoy the beauty of these iconic flowers year-round.
As you prepare to transplant your sunflower seedlings outdoors and witness their transition into full-grown plants, take pride in the journey you’ve undertaken and the knowledge you’ve gained along the way. With dedication, patience, and a little bit of green thumb magic, you’ll soon be rewarded with a bountiful display of sunflowers!
So go ahead, gather your supplies, sow those seeds, and let the beauty of sunflowers flourish in your garden. Happy planting!

Let me know!
What varieties of sunflowers will you be starting indoors this? Let me know in the comments below!